 打印本文
打印本文  关闭窗口
关闭窗口
Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of cadmium in contaminated rice by in vivo and in vitro bioassays
作者:庄萍等
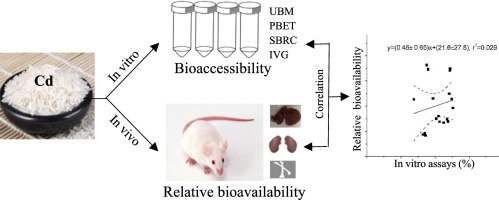
摘要:Consumption of rice is a major pathway of cadmium (Cd) exposure to humans with Cd bioavailability from rice being an important determinant of the potential health risk. We conducted both in vitro bioaccessibility (using four methods) and in vivo bioavailability (using a mouse model) of Cd from six rices. The relative bioavailability (RBA) for Cd ranged from 15 to 56%, 18 to 56% and 3.71 to 54% based on kidney, liver and femur, respectively, which was negatively correlated with total Cd concentration in contaminated rice (r2 = 0.74–0.94). Results of cadmium bioaccessibility in rice varied among different assays. When the relationship between the in vitro and in vivo data was assessed, all the correlations between the four in vitro methods and the mouse assay based on the liver or kidney were generally weak (r2=0.0006–0.52). Results of in vitro digestionmodels varied drastically among the different methods, suggesting that there were limitations for the in vitro methods to predict Cd relative bioavailability in contaminated rice. Together with the observation of poor correlations between
the in vivo and in vitro results, it is strongly suggested that further exploration andmore optimization of in vitro methods are required for use in human health risk assessment.
关键词:Cadmium Rice Bioavailability Bioaccessibility In vivo assay In vitro digestion
发表于:Science of the Total Environment 719 (2020) 137453
全文下载:/UploadFiles/file/202006/2020060516464637.pdf
 打印本文
打印本文  关闭窗口
关闭窗口