打印本文
打印本文  关闭窗口
关闭窗口 Multiple Exposure and Effects Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Population near Mining Area in South China
Zhuang P, Lu H, Li Z, Zou B, McBride MB (2014) Multiple Exposure and Effects Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Population near Mining Area in South China. PLoS ONE 9(4): e94484. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094484
Abstract
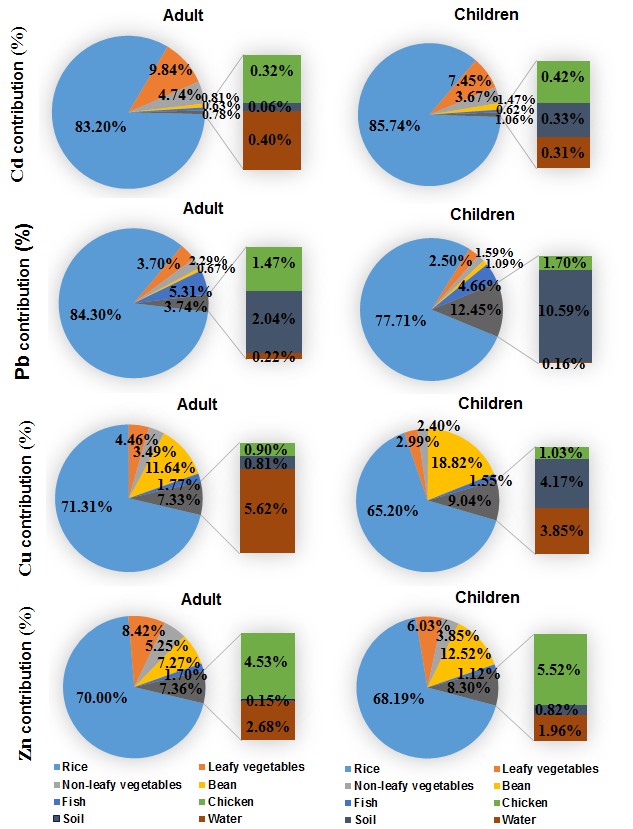
The objective of this study was to investigate the levels of Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in the environment and several important food sources grown and consumed in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine in Southern China, and evaluate potential health risks among local residents. The Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn concentrations of arable soils and well water near the mines exceeded the quality standard values. The concentrations of Cd and Pb in some food crops (rice grain, vegetable and soybean) samples were significantly higher than the maximum permissible level. The Cd and Pb concentrations in half of the chicken and fish meat samples were higher than the national standard. The residents living near Dabaoshan mine had higher Cd and Pb levels in hair than those of a non-exposed population. The intake of rice was identified as a major contributor to the estimated daily intake of these metals by the residents. The hazard index values for adults and children were 10.25 and 11.11, respectively, with most of the estimated risks coming from the intake of home-grown rice and vegetables. This study highlights the importance of multiple pathways in studying health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure in China.
全文下载:
http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0094484
 打印本文
打印本文  关闭窗口
关闭窗口