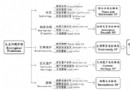
北京市生态安全格局及城市增长预景
在预景分析的基础之上,从城镇扩张趋势、生态安全维护用和地规模三方面对各预景进行定性和定量的分析与评价:
“无生态安全格局”下,城市建成区“摊大饼”式蔓延,周边组团与中心城区连片发展,生态资源占用较多。
“底线生态安全格局”下,由于生态安全格局严格的用地控制,保证了最低限度的生态基础设施核心网络和基本的生态服务。各城市组团虽没有完全连片,但趋势较为明显。
“满意生态安全格局”下,较好地维护了生态基础设施和生态服务,组团间由生态用地相隔。
“理想生态安全格局”下,最大限度地保护生态基础设施和生态服务,建设用地被生态用地分割呈组团式发展。
通过预景发现,除高安全水平的“理想生态安全格局”之外,其他三种预景都能满足北京市土地利用总体规划预测的2020年3800km2[ 《北京市土地利用总体规划(2005-2020)》中确定到2020年北京市城乡建设用地规模为3800 km2]建设用地的要求(见表3)
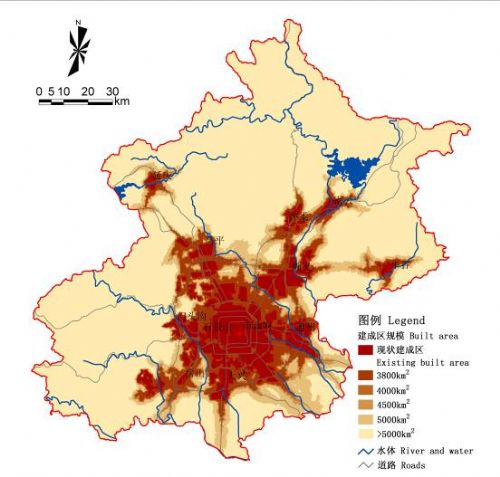
图8 无安全格局:“无态安全格局”情况下城镇空间格局
Fig.8 Urban Growth Pattern without Ecological SP
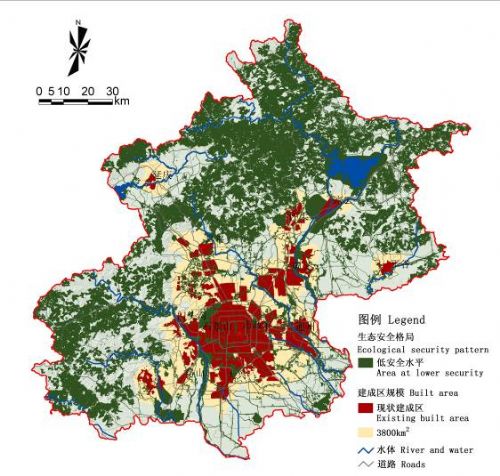
图9 底线格局:基于“底线生态安全格局”的城镇空间格局
Fig.9 Urban Growth Pattern Based on Minimum Ecological SP
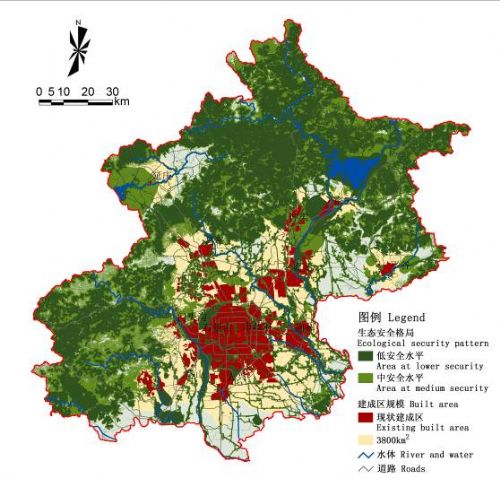
图10满意格局:基于“满意生态安全格局”的城镇空间格局
Fig.10 Urban Growth Pattern Based on Satisfying Ecological SP
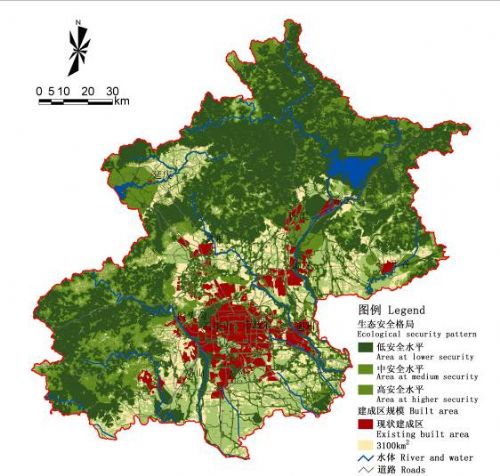
图11理想格局:基于“理想生态安全格局”的城镇空间格局
Fig.11 Urban Growth Pattern Based on Ideal Ecological SP
表3 各预景综合比较
Fig.3 The comprehensive comparison of the four scenarios
|
预景 Scenario |
预景1:无安全格局 Scenario 1: Urban growth pattern without ecological SP |
预景2:底线格局: Scenario 2: Urban growth pattern based on minimum ecological SP |
预景3:满意格局 Scenario 3: Urban growth pattern based on satisfying ecological SP |
预景4:理想格局 Scenario 4: Urban growth pattern based on ideal ecological SP n |
|
城镇扩张趋势 Urban growth pattern |
“摊大饼”式蔓延,通州、亦庄、顺义、石景山、房山、大兴等周边组团与中心城区连片发展,建设用地沿道路扩张趋势明显,远郊区县发展缓慢。The downtown area and clusters are combining as a whole. Construction land will mainly develop along main roads. The suburb new towns will develop slowly. |
建设用地间有少量生态基础设施用地,中心城区与周边组团融为一体,远郊区县发展速度较快。Within a green framework, clusters and downtown area are combining as a whole. The suburb new towns will grow quickly. |
建设用地发散式扩张,组团式分布,组团间由生态基础设施用地相隔,中心城区与周边组团融为一体,边界模糊,远郊区县发展速度较快。The green network forms an infrastructure that link central cities and surrounding clusters. The suburb new towns will grow quickly. |
建设用地被生态基础设施用地分割呈星群型或节点型发展。建设用地点缀在开放空间基质中,单个组团规模较小。Urban area will be broken by the green network. Construction lands will be surrounded by open space and the scale of individual cluster is small. |
|
生态安全维护 Ecological security |
关键生态过程的完整性得不到最低限度的保障,生态服务得不到基本的保障。The integrity of the critical ecological processes is not protected at the minimum level, which can not provide essential, ecosystems services |
关键生态过程的完整性得到最低限度的维护,近期的生态服务得到基本的保障。。The integrity of the critical ecological processes will be protected at the minimum level, which can provide essential ecosystems services |
关键生态过程的完整性得到较好的维护,生态服务可望在长时间内持续。The integrity and continuity of the critical ecological processes will be protected at the satisfying level, which can provide essential and sustainable ecosystems services |
关键生态过程的完整性得到较好的维护,生态服务可望在长时间内持续并不断改善。The integrity and continuity of the critical ecological processes will be protected at the ideal level, which can provide and enhance essential and sustainable ecosystems services |
|
用地规模 Land use allocation |
各类用地规模缺乏规划调控,规模难以预测。The amount and allocation of land uses are difficult to predict and control. |
可提供建设用地和农用地约8605km2,可以同时满足建设用地、生态用地、基本农田用的要求。The competing demands of different land uses can be fulfilled, providing a total area of 8605 km2 for construction and agriculture. |
可提供建设用地和农用地约4826km2,可以同时满足生态用地、建设用地、基本农田用地的要求。The competing demands of different land uses can be fulfilled, Providing a total area of 4826 km2 for construction and agriculture. |
可提供建设用地约2431km2,在生态优先和严格保护基本农田的前提下,建设用地需做出让步。The Ecological and agricultural land uses will be strictly protected and the demand for construction will not fully fulfilled, providing a total area of 2431 km2 for construction. |
4 结论与讨论
(1)本研究强调生态安全格局在空间结构上的完整性和在生态系统服务上的综合性。作为向城市提供自然服务的生态基础设施,生态安全格局应将生态系统的各种服务,包括旱涝调节、生物多样性保护、休憩与审美启智,以及遗产保护等整合在一个完整的景观格局中,落实在土地上。
(2)本研究在景观安全格局和生态基础设施理论指导下,提出了城市生态安全格局的研究框架。运用GIS空间分析等技术,对区域关键的生态过程(包括非生物自然过程、生物过程和人文过程)进行垂直和水平分析,判别维护生态过程安全的关键性空间格局,并整合为具有综合功能的生态安全格局。本文的生态安全格局包含了其他相关景观过程的安全格局,目的是强调生态安全格局的重要性和作为其他景观过程和格局的基础。而通常情况下,生态安全格局可以被看作是整体景观安全格局的一部分。
(3)生态安全格局的研究成果可直接指导城乡空间布局和生态建设。将生态安全格局与城市总体规划、土地利用规划、限建区规划、城市“绿线”规划相结合,作为它们的科学基础和核心内容,是生态安全格局理论对城市规划的重要贡献。
(4)通过北京城市格局发展预景分析,可以证明生态安全格局途径是实现“精明的保护”与“精明的增长”的有效途径。城市扩张的预景揭示了如何在有限土地资源条件下,实现保护与发展和谐同步的可能性。研究证明进行生态环境保护并不在于必须牺牲很多或更多的建设用地,也不必以牺牲土地利用的经济价值为代价,而是可以通过科学合理的空间格局的设计,用尽可能少的土地,来获得尽量好的生态效益;这一预景还揭示了城市的空间格局是土地的生态过程和格局所界定的,而不应该用一个意象的城市空间形态来规划。这正是城市“反规划”的核心理念[43~44],即:城市的发展建设规划必须以生命土地的过程和格局为依据和基础,先做不建设规划,再根据社会经济发展需要进行建设用地规划和布局。
(5)到目前为止,生态学理论研究如何转化为应用仍处于探索阶段,在今后的研究中单一安全格局的构建以及边界的确定方法将是重点研究的问题,生态安全格局低、中、高三种安全水平的划分依据也值得继续探讨和完善。
致谢:
参与本次研究的还包括:曹燕群、陈春娣、佘依爽、孙齐、乔青、宋吉涛、李青、李婷、胡望舒、熊亮、姬婷、李云圣、汤敏、廖慧仪、胡佳文、钟晨等。
感谢北京市国土资源局张维,陶志红和规划勘测中心全体同仁在项目全程给予的大力支持!
感谢王放、冯永锋、张峻峰、武弘麟、韩光辉、韩茂莉、吕植等人的指导和帮助!
References:
[1] Sustainable development strategy research group, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Report on sustainable development strategy of China, 2005. Beijing: Science Press, 2005. 81-84.
[2] Zube E.H. Greenways and the US National Park system. Landscape and Urban Planning Greenways,1995,33(1-3): 17-25.
[3] Ahern J. Greenways as a planning strategy. Landscape and Urban Planning Greenways,1995,33(1-3): 131-155.
[4] Walmsley A. Greenways: multiplying and diversifying in the 21st century. Landscape and Urban Planning, Greenway Planning around the World,2006,76(1-4): 252-290.
[5] Fabos J G,Ryan R L . International greenway planning: an introduction. Landscape and Urban Planning, International Greenway Planning,2004,68(2-3): 143-146.
[6] Benedict M A, McMahon E T . Green infrastructure: smart conservation for the 21st century. Washington, D.C.: Sprawl Watch Clearinghouse, Monograph Series. Website: www.sprawlwatch.org/greeninfrastructure.pdf
[7] Xiao D N, Chen W B, Guo F L. On the basic concepts and contents of ecological security. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002,13(3):354-358.
[8] Zou C X, Shen W S. Advances in ecological security. Rural Eco-Environment, 2003, 19(01):56-59.
[9] Cui S H, Hong H S, Huang Y F, Xue X Z. Progress of the ecological security research, 2005, 25(04): 861~868.
[10] Chen X, Zhou C H. Review of the Studies on Ecological Security. Progress in Geography, 2005, 24(06):8-20.
[11] Dong W, Zhang X H, Su D, et al.. Progress on Forewarning of Ecological Secur ity. Environmental Science and Technology, 2007, 30(12):97-99.
[12] Zhang H , Ma W Ch , HO Hon-Hing. Recent advances in research on LUCC: based urban ecological security, 2007, 27(05): 2109~2117.
[13] Ma KeMing, Fu BoJie, Li XiaoYa, Guan WenBing. The regional pattern for ecological security: the concept and theoretical basis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(4):761–768.
[14] Li X Y, Ma K M, Fu B J, Niu S K, The regional pattern for ecological security (RPES) : designing principles and method. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(5):1055–1062.
[15] Forman RTT. Land Mosaics : The Ecology of Landscapes and Regions. Cambridge :Cambridge University Press,1995.
[16]Yu K J. Security patterns and surface model in landscape ecological planning. Landscape and Urban Planning,1996,36(1): 1-17.
[17] Yu K J. Landscape ecological security patterns in biological conservation. ACTA ECOLOGICAS INICA, 1999, 19(01):8-15.
[18] Yu K-J, Ye Z, Li D H, et al. Connectivity of Landscape Ecological Process and Patterns: A Case Study at Zhongshan City, Guangdong Province. Urban Planning, 1998, 22(04):14-17.
[19] Yu K-J, Li D H, Huang Gang, Liu H L. Construction and organization of the landscape networks: discussion on the landscape ecological planning of the Beijing Shihua-Cave scenic area. Urban Planning Forum, 2005(03): 76-81.
[20] Yu K J, Li D H, Liu H L, et al . Growth pattern of Taizhou city based on ecological infrastructure: a negative app roach physical urban planning . City Planning Review, 2005, 29 (9): 76 -80.
[21] Yu K J , Zhang L. Ecological infrastructure as unbuildable zone and urban green space system: a case study of Heze. City Planning Review, 2007, 31(12):89-92.
[22] Yu K J , Xi X S , Wang S S. Townscape planning based on ecological infrastructure: a case study of Weihai, Shandong. City Planning Review, 2008, 32(3):87-92.
[23] Yu K J, Han X L, Zhu Q. Ecological Infrastructure as a Synthetic Solution to Urban Environmental Problems. JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES, 2007, 22(05):808-816.
[24] Wang B, Guan W B, Wu J A, et al. A Method for Assessing Regional Ecological Security Pattern to Conserve Biodiversity —— GAP Analysis. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 13(01):192-196.
[25] Guo M , Xiao D N , Li X. Changes of landscape pattern between 1986 and 2000 in Jiuquan oasis , Heihe River basin. ACTA ECOLOGICA SINICA, 2006, 26(02):457-466.
[26] Cen L D , LU Yi-he, TIAN Hui-ying1, SHI Qian. Principles and methodology for ecological rehabilitation and security pattern design in key project construction. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, Mar. 2007, 18 (3): 674 – 680.
[27] Gao Q C, Chen L D, Lü Y H, et al.. Regional Pattern for Ecological Security in Shanxi Section Along West-East Gas Pipeline Project. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 19(04): 164-172.
[28] Li Y H , Hu Z B, Gao Q, et al.. Ecological safety pattern of spatial extension in Shenyang City. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 26 (6) : 875 – 881.
[29] Fang S B, Xiao D N, An S Q. Regional ecosecurity pattern in urban area based on land use analysis :A case study in Lanzhou. CHINESE JOURNAL OF APPL IED ECOLOGY, 2005, 16 (12)∶2284~2290.
[29] Zhou W H, Zhang K F, Wang R S. Urban water ecological footprint analysis———a case study in Beijing, China. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2006, 26(9): 1524-1531.
[30] Niu L L, Ding G D. Study on Sustainable Use of Soil Resources in Beijing. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 13(05):175-179.
[31] Zhou W H , Wang R S. Methodology assessment of urban ecological security: A case study of Beijing. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(7): 848-852.
[32] Zhou W H, Wang R S. An entropy weight approach on the fuzzy synthetic assessment of Beijing urban ecosystem health, China. ACTA ECOLOGICA SINICA, 2005, 25(12):3244-3251.
[33] Steinitz C. A framework for theory applicable to the education of landscape architects (and other design professionals). Landscape Journal. 1990, 9(2): 136-143.
[34] Beijing Water Authority ed. Flood and drought hazards in Beijing. Beijing: China WaterPower Press, 1999. Pic. 30,32,4,44.
[35] Liu X C, Kang M Y. Analysis of functions and development countermeasures of urban Greenland system in China——Beijing case. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2001, 11(04):87-89.
[36] Caro T. Focal species. Conservation Biology, 2000, 14 (6):1569–1570.
[37] Opdam P, Verboom J, Pouwels R. Landscape cohesion: an index for the conservation potential of landscapes for biodiversity. Landscape Ecology, 2003, 18 (2): 113–126.
[38] Thomas B, Kennedy E. Conservation biology: Biodiversity barometers. Nature, 2004, 431(7012): 1046-1047.
[39] Lambeck, R J. Focal species: A multi-species umbrella for nature conservation. Conservation Biology, 1997, 11 (4), 849–56.
[40] Noss R F, Strittholt J R, Vance-Borland K, Carroll C, and Frost P. A conservation plan for the Klamath-Siskiyou ecoregion. Natural Areas Journal, 1999, 19:392–411.
[41] Yu K J, Li W, Li D H, Li C B, Huang G, Liu H L. Suitability analysis of heritage corridor in rapidly urbanizing region: a case study of Taizhou City. Geographical Research, 2005, 24(01): 69-76.
[42] Zhu Q, Yu K J, Li D H. The width of ecological corridor in landscape planning. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2005,25(9):2406-2412.
[43] Yu K J, Li D H, Han X L. On Negative Planning, City Planning Review, 2005, 29(09):64-69.
[44] Yu K J, Li D H. The Negative Approach. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2005:11-26.
参考文献:
[1] 中国科学院可持续发展战略研究组.2005中国可持续发展战略报告.北京:科学出版社,2005:80~84.
[7] 肖笃宁,陈文波,郭福良 等. 论生态安全的基本概念和研究内容. 应用生态学报,2002,13(03) :354~358.
[8] 邹长新,沈渭寿. 生态安全研究进展. 农村生态环境,2003,19(01):56~59.
[9] 崔胜辉,洪华生,黄云凤 等. 生态安全研究进展. 生态学报,2005,25(04): 861~868.
[10] 陈星,周成虎. 生态安全:国内外研究综述. 地理科学进展,2005,24(06):8~20.
[11] 董伟,张向晖,苏德 等. 生态安全预警进展研究. 环境科学与技术,2007,30(12) :97-99.
[12] 张浩, 马蔚纯, HO Hon Hin. 基于LUCC的城市生态安全研究进展. 生态学报,2007,27(05): 2109~2117.
[13] 马克明,傅伯杰,黎晓亚 等. 区域生态安全格局:概念与理论基础. 生态学报,2004,24(04): 761~768.
[14] 黎晓亚,马克明,傅伯杰 等. 区域生态安全格局:设计原则与方法. 生态学报,2004,24 (05): 1055~1062.
[17] 俞孔坚. 生物保护的景观生态安全格局. 生态学报,1999,19(01):8~15.
[18] 俞孔坚,叶正,李迪华 等. 论城市景观生态过程与格局的连续性——以中山市为例. 城市规划,1998,22(04):14~17.
[19] 俞孔坚,黄刚,李迪华 等. 景观网络的构建与组织——石花洞风景名胜区景观生态规划探讨. 城市规划学刊,2005,29(03):76~81.
[20] 俞孔坚,李迪华,刘海龙 等. 基于生态基础设施的城市空间发展格局——“反规划”之台州案例. 城市规划,2005(09) : 76 ~80.
[21] 俞孔坚,张蕾. 基于生态基础设施的禁建区及绿地系统——以山东菏泽为例. 城市规划,2007,31(12) :89~92.
[22] 俞孔坚,奚雪松,王思思 等. 基于生态基础设施的城市风貌规划——以山东省威海市城市景观风貌研究为例. 城市规划,2008,32(03) :87~92.
[23] 俞孔坚,韩西丽,朱强 等. 解决城市生态环境问题的生态基础设施途径. 自然资源学报,2007,22(05):808~816.
[24] 王棒,关文彬,吴建安 等. 生物多样性保护的区域生态安全格局评价手段——GAP分析. 水土保持研究,2006,13(01) :192~196.
[25] 郭明,肖笃宁,李新 等. 黑河流域酒泉绿洲景观生态安全格局分析. 生态学报,2006,26(02) :457~466.
[26] 陈利顶,吕一河,田惠颖 等. 重大工程建设中生态安全格局构建基本原则和方法. 应用生态学报,2007,18(03) : 674 ~680.
[27] 高启晨,陈利顶,吕一河 等. 西气东输工程沿线陕西段区域生态安全格局设计研究. 水土保持学报,2005,19(04):164~172.
[28] 李月辉,胡志斌,高琼 等. 沈阳市城市空间扩展的生态安全格局. 生态学杂志,2007,26(06) : 875 ~881.
[29] 方淑波,肖笃宁,安树青 等. 基于土地利用分析的兰州市城市区域生态安全格局研究. 应用生态学报,2005,16(12)∶2284~2290.
[30] 牛兰兰,丁国栋. 北京市土地资源可持续利用研究. 水土保持研究,2006,13(05) :175~179.
[31] 周文华,王如松. 城市生态安全评价方法研究——以北京市为例. 生态学杂志,2005,24(07) : 848~852.
[32] 周文华,王如松. 基于熵权的北京城市生态系统健康模糊综合评价. 生态学报,2005,25(12) : 3244 ~3251.
[34] 北京市水利局编.北京水旱灾害.北京:中国水利水电出版社,1999. 彩图30、32、42、44.
[35] 刘肖骢,康慕谊. 试析我国城市绿地系统的功能及其发展对策——以北京市为例. 中国人口.资源与环境,2001,11(04):87~89.
[41] 俞孔坚,李伟,李迪华 等. 快速城市化地区遗产廊道适宜性分析方法探讨——以台州市为例. 地理研究,2005,24(01):69~76.
[42] 朱强,俞孔坚,李迪华. 景观规划中的生态廊道宽度.生态学报,2005,25(9):2406~2412.
[43] 俞孔坚,李迪华,韩西丽. 论“反规划”. 城市规划,2005,29(09): 64~69.
[44] 俞孔坚,李迪华,刘海龙. “反规划”途径. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2005:11~26.
|
延伸阅读
|